Tinea
Tinea is a fungus that can grow on your skin, hair or nails. It is also spread through contact with infected skin or infected objects. Tinea infections are named for the part of the body they infect.
- Tinea capitus is when the head and hair are infected causing round bald patches.
- Tinea pedis is also known as “athletes foot” and may cause red, cracked, itchy skin between the toes or on the sole of the foot.
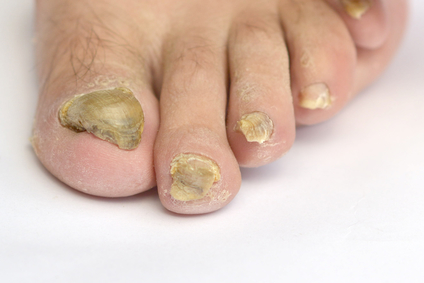
- Tinea unguim - infection in the nails causing thick, crumbly, yellowish nails.
- Tinea cruris - “jock itch”, is the name when fungus affects the warm, moist skin of the groin.
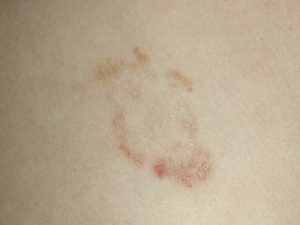
- Tinea corporis or ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin. It looks like a circle and spreads out leaving normal looking skin in the center of a raised reddish, scaly border.
- Tinea Versicolor is a surface yeast infection that causes changes in the outer most layers of the skin. It is caused by a yeast-like fungus normally found on our skin in small numbers. When overgrowth occurs, a rash appears as scaly white to tan spots over the upper arms, chest, back and neck. After sun exposure, these spots are more noticeable because they do not tan. With this type of tinea infection, it is important to remember that the infection will be cured in a week, however, the loss of color can last for months.
Diagnosis
Tinea can be diagnosed by any of the following:
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) preparation - A Sample of skin is taken by lightly scraping the infected area. The skin sample is placed on a slide with KOH solution. This solution slowly dissolves the cells but not the fungus cells. The fungus cells can then be seen with a microscope.
- A Wood's Light Exam - This test may be used to see if the rash is caused by a fungus. Your doctor will shine a special light on your skin where you have the rash. Certain kinds of fungi glow under this light.
- A fungal culture (Skin Culture) - This test can identify the type of fungus that is causing your infection.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of the infection the physician will give a prescription topical antifungal and/or an oral antifungal. Avoid walking barefoot and sharing garments with others. Wear loose-fitting garments made of cotton or synthetic materials designed to wick moisture away from the skin. Airing and drying the shoes will typically cause the fungus to die.
Give us a call Today
Call to schedule an appointment to discuss the best treatment option for you.




